|
Subcloning:
PDF format
|
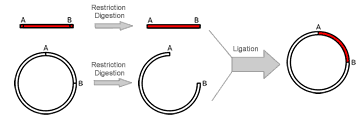
Subcloning is a technique used to move a particular gene of interest from a parent vector to a destination vector in order to further study its functionality. |
 |
| |
|
PCR Cloning:
PDF format
|
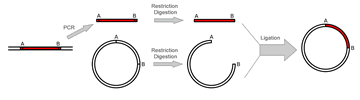
Use PCR reactions to amplify a insert DNA fragment, followed by sub-cloning (restriction endonuclease digestion of insert and vector DNA and fragment ligation). |
 |
| |
|
Gene Synthesis Cloning:
PDF format
|
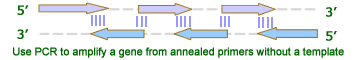
Use DNA oligos and PCR reactions to synthesize a gene without source DNA as template followed by Subcloning (restriction endonuclease digestion and fragment ligation). |
 |
| |
|
TA TOPO Cloning:
PDF format
|
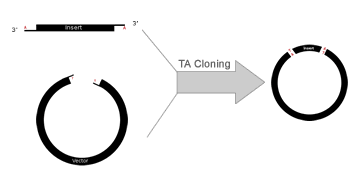
TA Cloning is a subcloning technique that doesn't use restriction enzymes and is easier and quicker than traditional subcloning. |
 |
| |
|
Directional TOPO Cloning:
PDF format
|
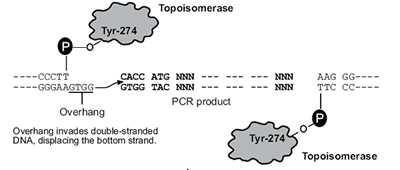
Use PCR reaction to amplify a DNA fragment. The resulting PCR products have four additional bases (CACC) at the 5´ ends that are from the specially designed forward PCR primer. With a special ligation
kit, this fragment is directly ligated into a linearized vector DNA (D-TOPO Vector, which contains GTGG overhangs at the 5’ end) without pre-digestion with restriction endonucleases. The fragment can only be inserted
in forward orientation. |
 |
| |
|
Gateway Cloning:
PDF format
|
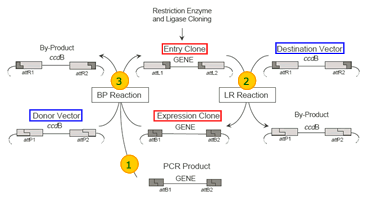
This is a cloning method based on the site specific recombination of lambda bacteriophage. |
 |