BxSeqTools Ultimate Molecular Cloning Guides - Subcloning
| PCR Cloning is similar to subcloning, except that the insert is first amplified through PCR reaction. |
 |
PCR Cloning Construct and Primer Design with BxSeqToolsAdvantages of using BxSeqTools for PCR cloning design:
|
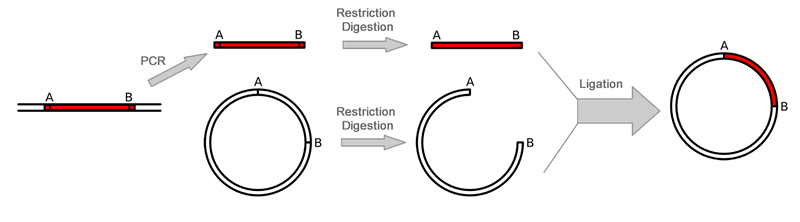
Overall PCR Cloning ProceduresThe gene is first amplified using Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Restriction enzymes are then used to excise the gene of interest (the insert) from the parent. The insert is purified in order to isolate it from background junk. A common purification method is gel isolation. Simultaneously, the same or compatible restriction enzymes are used to digest (cut) the destination. The idea behind using the same restriction enzymes is to create complementary sticky ends, which will facilitate ligation later on. A phosphatase (commonly Calf Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase; CIAP) is also added to prevent self-ligation of the destination vector. The digested destination vector is isolated/purified. The insert and the destination vector are then mixed together with DNA ligase. A typical ratio of insert genes to destination vectors is 3:1; by increasing the insert concentration, self-ligation is further decreased. After letting the reaction mixture sit for a set amount of time at a specific temperature (dependent upon the size of the strands being ligated; for more information see DNA ligase), the insert should become successfully incorporated into the parent plasmid.
|