|
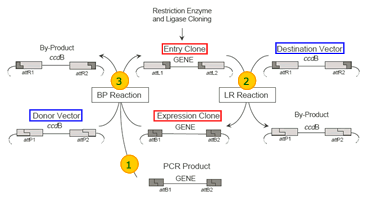
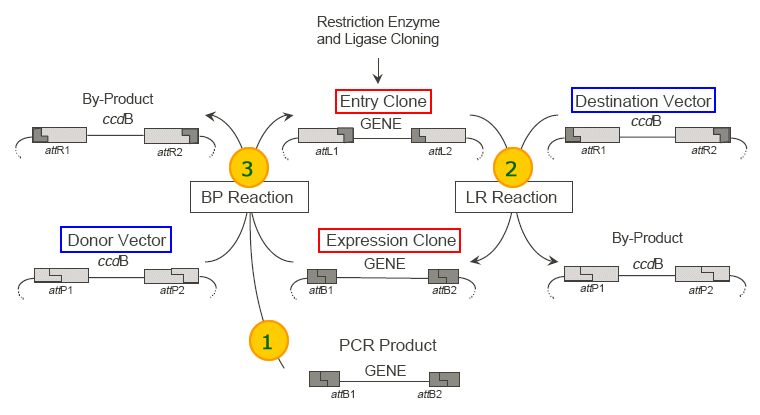
Gateway is a cloning method based upon the site specific recombination of lambda bacteriophage.
Two types of recombination sites have been engineered to recombine uniquely between the two ends of a source sequence and a host vector. The sites have also been engineered to allow the recombination reactions to be
completely reversible using two sets of catalytic proteins. These two reactions are called LR and BP, so named because of the recombination sites involved in each reaction: LR
recombines attL and attR sites, BP recombines attB and attP sites. The recombined sites transform by swapping opposite halves into the opposite set, so attL and attR become attB and attP and vice versa.
Vectors engineered to contain these sites have been given the names: Entry Clone, Expression Clone, Donor Vector, and Destination Vector.
| LR reaction |
BP reaction |
| Takes a sequence of interest in a transcriptionally silent Entry Clone, recombines it with an antibiotic resistant Destination Vector to produce a transcriptionally active Expression
Clone. |
Takes a sequence of interest from an Expression Clone, recombines it with a Donor Vector to produce an Entry Clone for further cloning. |
 |
 |
|
|
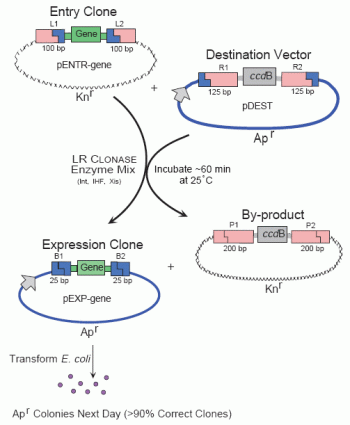
Gateway Technology uses lambda phage-based site-specific recombination instead of restriction endonuclease and ligase to insert a gene of interest into an expression vector. The DNA recombination sequences (attL,
attR, attB, and attP) and the LR and BP Clonase enzyme mixtures that mediate the lambda recombination reactions are the foundation of Gateway Technology. Transferring a gene into a destination
vector is accomplished in just two steps:
Step 1: Clone the gene of interest into an entry vector:
- Using restriction endonucleases and ligase.
- Starting with a cDNA library prepared in an attL Entry Vector.
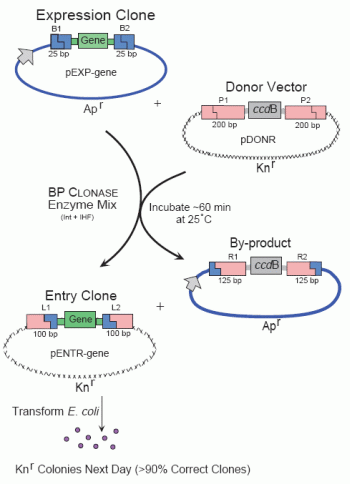
- Using an Expression Clone from a library prepared in an attB expression vector via the BP Reaction.
- Recombinational cloning of PCR fragment with terminal attB sites, via the BP Reaction.
Step 2: Mix the Entry Clone containing the gene of interest in vitro with the appropriate Gateway expression vector (Destination Vector) and
Gateway LR Clonase enzyme mix. Site-specific recombination between the att sites generates an Expression Clone and a by-product.
Step 3: Mix the Expression Clone or PCR products flanked by attB sites with Donor Vector to generate new Entry Clone, via BP Reaction.
|